Hearing Aids
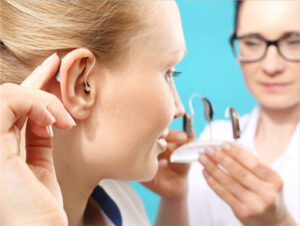
Hearing loss is a common problem, and can greatly affect relationships as well as quality of life. Genetic factors make some people more prone to developing hearing loss. Illness and continuous exposure to loud noise all damage the delicate inner ear structures. As you reach your senior years, you’re much more likely to have hearing loss.
Heart disease, high blood pressure and diabetes can also increase the risk of hearing loss, as blood supply to the ears is reduced. Medications like antibiotics, diuretics, chemotherapy drugs and drugs for erectile dysfunction can also contribute to hearing loss.
In some cases, surgery may reverse hearing loss caused by scar tissue, infection or otosclerosis (abnormal bone tissue in the ear). Mechanical causes of hearing loss can be treated by reconstructive surgery of the outer and middle ear. Hearing aids also help sound reach the inner ear, and are the most effective way to treat hearing loss.
Is it Time for Hearing Aids?
Hearing aids are devices built to capture, process and amplify sound from the environment into the inner ear. These devices work by capturing sound waves from the environment using tiny microphones. The sound waves are then processed to eliminate any static and background noise. Tiny speakers will then broadcast these sounds into the inner ear at the correct decibel level – thereby compensating for hearing loss.
Hearing Aid Types
Hearing aids come in a variety of styles, designs, and functions. While there may be hype about the “best” hearing aids, the quality of sound and comfort are most important factors in choosing hearing aids.
Types of hearing aids include:
- Completely in the canal (CIC): Fit inside your ear canal.
- In the canal (ITC): Fit partially inside your ear canal.
- In-the-ear (ITE):- Fills most of the outer ear or just the lower half.
- Behind-the-ear (BTE): Hooks over the top of your ear and rests behind the ear.
- Receiver-in-canal (RIC) and receiver-in-the-ear (RITE): Same as BTE, but with the speaker or receiver inside the ear canal.
- Open fit: Similar to the BTE, but with a thin tube entering the ear canal.
What to Expect from Hearing Aids
While hearing aids help improve hearing, it’s important to note that they do not restore natural hearing. Sounds will still seem rather muted and the sound quality will need fine-tuning.
Hearing aid technology is rapidly evolving, and today’s hearing aids have functions such as remote control, Bluetooth connectivity, wireless access, telecoils, noise cancellation, multidirectional microphones, and more that will continue to improve the quality of hearing.
Learning how to use your hearing aid will take time. You’ll need to monitor your hearing to adjust the aid upward or downward.
In selecting a hearing aid, make sure that it feels comfortable, as you will be wearing it the rest of your life. A hearing aid will improve your hearing and your quality of life.
Contact our office:
To find out more about our Hearing Aid services, visit Dr. Schneiderman’s office located at 215 Union Avenue – Suite C, Bridgewater, NJ 08807, or book an appointment by calling us at (908) 725-5050.

